
Nervous System Overview
1. Neurons: The primary excitable cells of the nervous system that generate and propagate electrical signals.
- Parts of a Neuron:
- Cell Body (Soma): Contains the nucleus and organelles; responsible for the synthesis of proteins and other cellular components.
- Dendrites: Short, branched extensions that receive signals from other neurons.
- Axon: A long extension that transmits electrical impulses away from the cell body. Axons can vary in length from a few millimeters to over a meter.
- Neurites: Collective term for dendrites and axons.
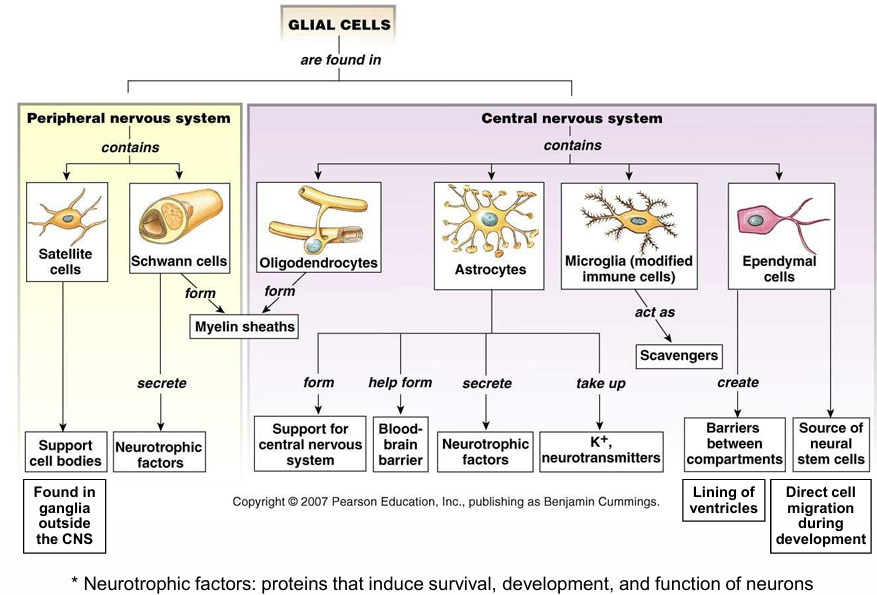
2. Glial Cells (Glia): Non-neuronal cells that provide support and protection for neurons.
- Types of Glial Cells:
- Astrocytes: Provide structural support, form the blood-brain barrier (BBB), and regulate neurotransmitter levels.
- Oligodendrocytes: Form the myelin sheath in the central nervous system (CNS).
- Microglia: Act as immune cells in the CNS, clearing debris and dead cells.
- Ependymal Cells: Line the ventricles of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord, producing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
- In the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS):
- Schwann Cells: Form the myelin sheath around peripheral nerves.
- Satellite Cells: Support neuron cell bodies in ganglia.

Neuronal Morphology and Function
- Excitability: Neurons are excitable cells that generate action potentials to communicate signals.
- Signal Transmission:
- Dendrites receive incoming signals.
- Cell Body integrates these signals.
- Axon transmits the integrated signal to other neurons or muscles.
Staining Techniques
- Nissl Stain: Visualizes cell bodies by staining the nucleus and surrounding material.
- Golgi Stain: Fills the entire neuron with a dark color, allowing visualization of the entire structure, including dendrites and axons.
Cytoskeleton of Neurons
- Microtubules: Provide structural support and are involved in axonal transport.
- Neurofilaments: Provide tensile strength.
- Microfilaments (Actin Filaments): Involved in changing the shape of the neuron.
Axonal Transport
- Fast Axonal Transport: Moves materials (like neurotransmitter-filled vesicles) quickly along the axon (up to 400 mm/day).
- Slow Axonal Transport: Moves cytoskeletal components and enzymes more slowly (1-2.5 mm/day).
Synaptic Transmission
- Synapse: Junction between neurons where neurotransmitters are released from one neuron and received by another.
- Pre-Synaptic Terminal: The end of the axon where neurotransmitters are released.
- Post-Synaptic Dendrite: Receives the neurotransmitter signal via specific receptors.
Types of Neurons
- Sensory Neurons: Carry information from sensory receptors to the CNS.
- Motor Neurons: Transmit signals from the CNS to effectors like muscles.
- Interneurons: Connect neurons within the CNS.
Classifications of Neurons
- Based on structure:
- Unipolar, Bipolar, Multipolar, Anaxonic.
- Based on function:
- Sensory, Motor, Interneurons.
Glial Cells in Detail
- Astrocytes: Structural support, BBB formation, and ion balance.
- Oligodendrocytes: Myelination in the CNS.
- Microglia: Immune response in the CNS.
- Ependymal Cells: Line ventricles and produce CSF.
- Schwann Cells (PNS): Myelination in the PNS.
- Satellite Cells (PNS): Support neuron cell bodies in peripheral ganglia.
728x90
반응형
'BMI' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 멤브레인 전위 증가에 따른 전류 변화 (1) | 2024.10.14 |
|---|---|
| Action Potential 활동 전위 (0) | 2024.10.11 |
| Human Nervous System - CNS, Spinal cord (2) | 2024.09.02 |



